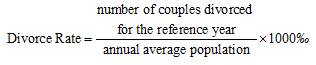
Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Health Care Institutions refer to the units which have been qualified with the Certification of Health Care Institution,, or qualified with the Certification of Corporate Unit by the civil affairs, administration for industry and commerce, and engaging in medical care services, disease control services, health supervision services, or medicine research and on-job training, etc., including: hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized public health institutions, and other health care institutions.
Hospitals include general hospitals, traditional Chinese medicine hospitals, hospitals of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine, nationalities hospitals, specialized hospitals and nursing hospitals, as well as affiliated hospitals of medical colleges, excluding specialized disease prevention and treatment institutes, maternal and child health centers and convalescent hospitals.
Health Care Institutions at Grass-root Level include community health service centers (stations), sub-district health centers, township health centers, village clinics, outpatient departments and clinics.
Specialized Public Health Institutions include CDC, specialized disease prevention and treatment institutions, maternal and children health centers, health education institutions, emergency centers (first-aid stations), blood gathering and supplying institutions, health inspection institutions, and family planning technical service institutions headed by the health department. It does not include infectious hospital, tuberculosis hospital, schistosomiasis control hospital, mental hospital, health supervision (monitoring and testing) institution.
Health Personnel refer to all employees engaged in the health care institutions, such as hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized public health institutions, and other health care institutions, including health technical personnel, village doctors and assistants, other technical personnel, administrative staffs and logistics technical workers. Data are based on the year end payroll, including personnel employed (including contract workers) and re-employed after retirement by the institution for more than 6 months, excluding temporary workers, retired personnel, resigned personnel, personnel who have left the institution but kept the contract relation and personnel who are re-employed after retirement or temporarily employed for less than 6 months.
Health Technical Personnel refer to the professional staff engaged in health care, including licensed physicians and physician assistants, registered nurses, pharmacists, laboratory and imaging technicians, health care supervisors and intern doctors, pharmacists, nurses, and technical personnel, excluding health technical personnel engaged in management (e.g. president, vice president and secretary of the party committee etc).
Licensed Physicians refer to the medical workers with licenses of qualified doctors and are employed in medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare institutions, excluding the licensed doctors engaged in management. The physicians are divided into 4 categories: clinician, Chinese medicine, stomatology and public health.
Licensed Physician Assistants refer to the medical workers with licenses of qualified assistant doctors and are employed in medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare institutions, excluding the licensed assistant doctors engaged in management. Physician assistants are divided into 4 categories: clinician, Chinese medicine, stomatology and public health.
Number of Health Technical Personnel per 1000 Population The formula is:
Number of health technical personnel per 1000 population = number of health technical personnel / population *1000
Number of Licensed Physicians & Physician Assistants per 1000 Population The formula is:
Number of licensed physicians & physician assistants per 1000 population = (number of licensed physicians + number of licensed physician assistants) / population *1000
Number of Beds refer to the actual number of beds in health care institutions at year-end, also known as the actual number of beds or hospital beds, including regular beds, simple beds, monitoring beds, extra bed over 6 months, beds under disinfection or repairing, beds deactivated due to expansion or overhaul, not including neonatal beds, pre-delivery beds, inventory beds, observation beds, temporary beds and family accompany beds.
Number of Beds of Health Care Institutions per 1000 Population the formula is:
Number of beds of health care institutions per 1000 population = number of beds of health care institutions at year-end / population at year-end *1000
Morbidity Rate of Class A and B Notifiable Infectious Diseases refers to the number of cases of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference year. The formula is:
Morbidity rate of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases = number of cases of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases / population *100000
Mortality Rate of Class A and B Notifiable Infectious Diseases refers to the number of deaths of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference year. The formula is:
Mortality rate of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases= number of deaths of Class A and B notifiable infectious diseases / population *100000
Maternal Mortality Rate refers to number of maternal deaths per 100,000 maternal. It generally refers to maternal mortality from the start of pregnancy to 42 days after parturition, due to pregnancy or any treatment of pregnancy. However, accidental deaths are not included. According to internationally accepted approach, the live births are used to represent the total number of maternity.
Mortality Rate of Children under 5 refers to the ratio of deaths of children under 5 in a year to the number of live births, and usually is presented by бы.
Neonatal Mortality Rate refers to the ratio of neonatal deaths in a year to the number of live births, and usually is presented by бы. Neonatal deaths refer to the deaths of new-birth within 28 days (0-27 days).
Total Health Expenditure refers to the total monetary value of health resources in a country or a region mobilized by the whole society for public health, calculated based on source approach. It reflects the attention and affordability of the government, society and individuals for public health, and the major characteristics, justice and rationality of the health fund-raising model under certain economic circumstance.
Government Health Expenditure refers to the expenditure of the governments at all levels on medical and health care services, medical subsidies, health administration and health security management, and undertakings of family planning etc.
Social Health Expenditure refers to all inputs of the society except the government in public health, including the expenditures on social medical security, commercial health insurance, private expenditure on of medical and health care operation, social donation and contribution, and income from administrative fees etc.
Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure refers to expenditure in cash on various health services by rural and urban residents, including self payments of residents within various medical insurance systems. It can be categorized as cash expenditure on health by urban and rural residents and reflects their affordability of public health.
Per Capita Health Expenditure refers to the ratio of total health expenditure in a year to the average population.
Ratio of Health Expenditure to GDP refers to the ratio of total health expenditure in a year to GDP, which indicates the financial support given by a nation to health work and the attention paid on the public health and the health of residents by the government and society.
Number of Civil Affairs Institutions with Accommodations refers to the number of social service institutions that can provide accommodations for the elderly, the disabled, the mentally handicapped and the mentally ill, and children. It includes social welfare institutions, assistance and support institutions for people in extreme difficulty, other pension institutions, social welfare hospitals, children's welfare homes, assistance and protection centers for minors, relief and management institutions for vagrants and beggars, resettlement farms and other institutions providing accommodations.
Number of Orphans refers to juveniles under the age of 18 that have lost or cannot find their parents. Orphans are affirmed by departments of civil affairs at county level according to relevant regulations, and receive orphan subsidies.
Number of Children Adopted refers to the total number of children adopted by families through adoption registration, including the total number of Chinese children adopted at home and abroad.
Adoption by Chinese Citizens refers to adoption of children by Chinese citizens (including residents from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, and overseas Chinese).
Adoption by Foreigners refers to adoption of children by foreign nationals (including stateless persons). Adoption by a couple with one being foreigner would be treated as adoption by foreigner.
Number of Urban Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of urban residents who have been included in the scope of local urban minimum living guarantee and have been granted subsidies by the end of the reporting period.
Number of Rural Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of rural residents who have been included in the scope of local rural minimum living guarantee and have been granted subsidies by the end of the reporting period.
Divorce Rate refers to ratio of divorced couples to the annual average population in a certain region for the reference year, the formula is:
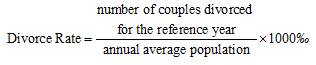
Number of Employed Person with Disabilities refers to the number of urban and rural persons with disability certificates who are actually employed through various forms of employment.