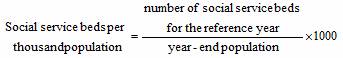
Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Medical and Health Care Institutions refer to the units which have been qualified the Certification of Health Care Institution, certification of family planning technical service by the administration of public health (family planning), or qualified the Certification of Corporate Unit by the civil affairs, administration for industry and commerce, commission office for public sector reform, and engaging in medical health care services, public health services, or medicine research and on-job training, etc., including: hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized public health institutions, and other medical and health care institutions.
Hospitals include general hospitals, hospitals specialized in traditional Chinese medicine, hospitals of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine, ethnic hospitals, specialized hospitals and nursing hospitals, excluding specialized disease prevention and treatment institutes, maternal and child health care hospitals and convalescent hospitals, including affiliated hospital of medical college.
Health Care Institutions at Grass-root Level include community health service centers, community health service stations, urban health centers, township health centers, village clinics, outpatient departments and clinics (health centers).
Specialized Public Health Institutions include centers for disease control and prevention, specialized disease prevention and treatment institutions, women and children care agencies(including women and children health care family planning service center), health education institutions, first aid centers, blood gathering and supplying institutions, health supervision and inspection agencies, and family planning technical service centers that obtained the Certification of Health Care Institution or certification of family planning technical service centers.
Other Medical and Health Care Institutions include sanatoriums, clinical laboratory centers, medicinal scientific research institutions, on-job training institutions, health supervision (monitoring, testing) institutions, medical examination centers, rural water improvement centers, talent exchange centers, and statistical information centers, etc.
Health Care Employees refer to all employees engaged in the health care institutions, such as hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized public health institutions, and other medical and health care institutions, including medical technical personnel, village doctors and assistants, other technical personnel, managerial and service staff. The data is based on the year end payroll, including personnel hired (including contract labor) and re-employed after retirement by the institution for over half a year and excluding temporary workers, retired personnel, resigned personnel, personnel who have left the institution but kept the contract relation and personnel who are re-employed after retirement or temporarily employed for less than half a year.
Medical Technical Personnel refer to the professional staff engaged in health care, including licensed doctors, licensed assistant doctors, registered nurses, pharmacists, laboratory technicians, imaging staff, health care supervisors and intern doctors, pharmacists, nurses, and technical personnel, excluding the medical technical personnel engaged in managerial job (e.g. president, vice president and secretary of the party committee etc).
Licensed Doctors refer to the medical workers who have obtained the licenses of qualified doctors and are employed in medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare institutions, excluding the licensed doctors engaged in management job. The licensed doctors are divided into 4 categories: clinician, Chinese medicine physicians, dentist and public health physicians.
Licensed Assistant Doctors refer to the medical workers who have obtained the licenses of qualified assistant doctors and are employed in medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare institutions, excluding the licensed assistant doctors engaged in management job. The classification of licensed assistant doctors is clinician, Chinese medicine, dentist and public health.
Number of Medical Technical Personnel per 1000 Population The formula is:
Number of Medical Technical Personnel per 1000 Population = Number of Medical Technical Personnel / Population *1000
The population is the figure of usual population at year-end.
Number of Licensed (Assistant) Doctors per 1000 Population The formula is:
Number of Licensed Doctors per 1000 Population = (Number of Licensed Doctors + Number of Licensed Assistant Doctors) / Population *1000
The population is the figure of usual population at year-end.
Number of Beds refer to the fixed actual beds (non authorized beds) at year-end, including regular beds, simple beds, monitoring beds, beds which are disinfected and repairing, beds deactivated due to expansion or overhaul, not including neonatal beds, predelivery bed, inventory bed, observation beds, temporary beds and family accompany beds.
Number of Beds of Medical and Health Care Institutions per 1000 Population the formula is:
Number of Beds of Medical and Health Care Institutions per 1000 Population = Number of Beds of Medical and Health Care Institutions / Population *1000
The population is the figure of usual population at year-end.
Incidence Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the incidence cases notifiable class A and class B infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference region in the reference year. The formula is:
Incidence Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases = Incidence Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases / Population *100000
Death Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the death cases notifiable class A and class B infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference region in the reference year. The formula is:
Death Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases= Death Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases / Population *100000
Mortality Rate of A and B Type Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the ratio of death cases notifiable class A and class B infectious diseases to the incidence cases in the reference region in the reference year. The formula is:
Mortality Rate of A and B Type Notifiable Infectious Diseases = Death Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases / Incidence Cases *100%
Crude Mortality Rate refers to the ratio of deaths to the average population in a year of the region, and usually is presented by ¡ë.
Fatality Rate refers to the ratio of deaths caused by a disease to the population infected by it in a given period (generally one year), and usually is presented by %.
Maternal Mortality Rate refers to number of maternal death per 10,000 maternal. Generally refers to maternal mortality from pregnancy to 42 days after parturition due to pregnancy or any treatment of pregnancy, however, accidental deaths are not included. According to internationally accepted calculation method, the live births are used to represent the total number of maternal.
Number of Live Births refers to the number of newborn having one of four indicators like heartbeat, breathing, umbilical cord pulsation and involuntary muscle contraction after childbirth with gestation of at least 28 weeks or above (if the gestation is not clear, then refer to the birth weight of 1000 grams and above).
Mortality Rate of Children under 5 refers to the ratio of deaths of children under 5 in a year to the number of live births, and usually is presented by ¡ë.
Newborn Mortality Rate refers to the ratio of neonatal deaths in a year to the number of live births, and usually is presented by ¡ë. Neonatal deaths refer to the deaths of new-birth under the age of 28 days (0-27 days).
Number of Persons Participated in the New Rural Cooperative Medical System refers to the number of persons who have given payment to the new cooperative medical system by the deadline of fundraising during the year according to the implementation plan of the new system.
Expenditure of Funds for the New Rural Cooperative Medical System This Year refers to expenditures on compensation funds for the new rural cooperative medical system from the fund account of new cooperative medical system this year.
Persons Benefited from the Compensation of New Rural Cooperative Medical System refers to the number of person-times of those who participate in the new system and have been compensated for medical treatment in the year, including hospitalization, family account form, out-patient, large special diseases out-patient, normal childbirth in hospital, medical examination and other compensations
Funds Raised for the New Rural Cooperative Medical System within the Reference Year refers to the amount of funds raised within the reference year and put into the special new rural cooperative medical account, including the matching funds of central and local governments, paid money by farmers (including relief funds paid by the civil affairs department and other relevant departments), all the interest income generated this year of the funds and funds actually raised from other channels this year. The amount of funding equals to the funds entering into the special new rural cooperative medical account, excluding the carry-over funds from the previous year.
Total Expenditure on Public Health refers to the total monetary value of health resources in a country or a region collected by the whole society for public health based on source approach. It reflects the attention and affordability of the government, society and individual for public health and the major characteristics, justice and rationality of the health fund-raising model under certain economic circumstance. .
Government Expenditure on Public Health refers to the expenditure of the governments at all levels on medical and health care services, medical subsidies, health administration and health insurance management, and undertakings of family planning etc.
Social Expenditure on Public Health refers to all inputs of society except the government in public health including the expenditures on social medical security, commercial health insurance, private expenditure on operation of medical and health care, social donation and contribution, and income from administrative fees etc.
Individual Cash Expenditure on Health refers to expenditure in cash on various health services by rural and urban residents, including self payments of residents within the system of multi-medical insurance. It can be categorized as cash expenditure on health by urban and rural residents and reflects their affordability of public health.
Average Expenditure on Health refers to the ratio of total expenditure on health in a year to the average population.
Ratio of Total Expenditure on Public Health to GDP refers to the ratio of total expenditure on public health in a year to GDP, which indicates the financial support given by a nation to health work and the attention paid on the public health and the health of residents by the government and society.
Licensed Social Workers refer to those who passed the National Aptitude Test for Social Workers and obtained the certificates.
Social Service Beds per Thousand Population refer to the total number of social service beds for the elderly, disabled, mentally-retarded, mentally-disabled, children, people in need and others divided by year-end population multiplied by 1000.
The formula is:
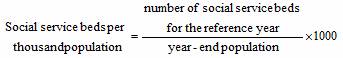
The number of beds for the elderly and disabled includes beds in urban institutions for aged persons, rural institutions for aged persons, social welfare homes, homes for disabled veterans, convalescent hospitals, military recreation habitation, community service institutions for honourable servicemen and sanatoriums for ex-servicemen. The number of beds for the mentally-retarded and mentally disabled includes beds in mental hospitals for ex-servicemen and the related beds in social welfare hospitals. The number of beds for children includes the beds in social welfare institutions for children and centers for rescuing street children. The number of beds for relief and other social service beds includes the beds in community pension service center, resettlement farm, community elderly care service center, salvation station, other adoption institutions, convalescent homes for retired military officers and military supply stations.
Military Supply Stations also called units of management of military supply. They are the general name of units such as military food supply stations, military water supply stations, servicemen transfer reception stations, which are managed by departments of civil affairs entrusted by local governments with independent accounting, and provide services to army during the war or peacetime.
Institutions Providing Services for Handicapped People refer to those welfare-oriented enterprises employing a significant number of handicapped people with certain labour ability (handicapped employees shall exceed 10% of the production staff). They can be categorized as welfare factories, artificial limb plants and other welfare enterprises. They can be in the form of state ownership, collective ownership or other kinds of ownership.
Number of Orphans refers to juveniles under age of 18 that have lost parents or can't find parents. Orphans are affirmed by department of civil affairs at county level according to relevant regulations, and have received orphan subsidies..
Number of Adoption Registration of Family Children refers to abandoned babies that can¡¯t find parents, children and orphans raised by welfare institutions adopted by Chinese citizens, or children adopted by foreign nationals, which have registered in department of civil affairs at county level and above, and gained legal adoption right. One registration means one case.
Adoption Registration of Chinese Citizens refers to adoption registration of children by Chinese citizens, which include persons from Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, and overseas Chinese.
Adoption Registration of Foreign Nationals refers to adoption registration of children by foreign nationals, which include stateless persons, or by couples, at least one of whom is of foreign national.
Number of Urban Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those urban residents whose average family income is below a minimum local standard, and status of family property meets the relevant regulation, and have received subsidies by the end of the reporting period
Number of Rural Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those rural residents whose average family income is below a minimum local standard, and receiving the minimum living allowances from the local government by the end of the reporting period.
Households Enjoying Five Guarantees refers to the elderly, disabled or under the age of 16 villagers, without working capacity, without the source of life, and without legal supporter, upbringing persons, brought up persons, or legal supporter, upbringing persons, brought up persons can not support, upbringing, bring up.
Number of Recipients of Traditional Relief refers to special personnel receiving support from civil affair department according to national regulations and personnel who resigned because of the streamlining in the 1960s. Special personnel include traditional recipients of civil affair support, such as lepers, insurrectionists and surrenders of former KMT, returned overseas Chinese, Taiwan compatriots, personnel pardoned and released early from prisons, personnel removed of the label ¡°rightist¡±, educated youth suffered from work injuries in the ¡°Down to the Countryside Movement¡± and personnel who have lost their work capacity due to family planning surgeries, and received subsidies.
Number of Service Institutions in Communities refers to the total number of community service guidance centers, community service centers, community service stations, community pension institutions, community mutual aid pension facilities and other community service institutions at the end of the reporting period. These institutions offer home keeping and elderly care services for the elderly, handicapped people, children and their families, like commodity delivery, health care, cleaning, adult day care, companion and others.
Coverage Rate of Service Institutions in Communities The formula is:
Coverage rate of service facilities in communities = number of service facilities in communities/number of village committees + communities¡Á100%
Crude Divorce Rate refers to ratio of divorced couples to the annual average population in a certain region for the reference year, the formula is:
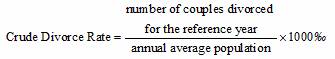
Handicapped School-age Children without School Attendance refers to the number of handicapped children of the school age in accordance with the Law on Compulsory Education (6 to 14 years old or 7 to 15 years old) who fail to attend any schools for various reasons as of December 31 of the current year.
New Job Created for the Urban Disabled refers to the new jobs created for the urban disabled through centralized employment, self-employment, employment of welfare posts, supported employment and other forms.
Centralized Employment refers to the employment of the urban handicapped residents, in a centralized manner, satisfying the conditions of centralized employment, by welfare enterprises, work and treatment agencies, blind massagists¡¯ centers and other organizations.
Proportionate Employment refers to the employment of the urban handicapped residents by governmental bodies, organizations, corporate and public institutions, and various economic organizations in a decentralized manner.
Individuals and Other Forms of Employment refer to individual employment and flexible employment of persons with disabilities in cities and towns.