Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Cultivated
Land refers
to land mainly for the regular cultivation of farm crops (including
vegetables), with some fruit trees, mulberry trees and others, covers
cultivated land, newly-developed land, reclaimed land, consolidated land,
fallow, beach land that can guarantee one harvest per year on average. It also
covers fixed ditch, canal, road and sill (ridge) with width less than 1 meter
in the South and 2 meters in the North, lands planted temporarily with herbs,
grass, flowers and nursery stocks, and other cultivated land with temporary
change of use.
Garden
Land refers
to land for intensive cultivation of perennial woody plants and herbs to
collect fruits, leaves, roots, stems and juice, with a covering rate over 50%
and plant number per mu over 70% of rational plant
number. Land for nursery is included.
Forestland
refers to land for planting arbor, bamboo,
bush shrub and land in coastal zones for planting mangrove. It includes slash,
but not the green belts in residential area, forests requested for railway and
highway, and the dike protection forest around rivers and ditches.
Pastureland
refers to land mainly for the growth of herbs.
Volume
of Runoff refers to the total volume of water running through a certain cross section of a
river during a certain period of time, reflecting the water resource condition
in a country or a region. The formula for calculating volume of runoff is as
follows:
Runoff =Precipitation-Evaporation
Drainage
Area Each river has its own main stream and branches to form the water system of
the river. Each river has its own catchment’s area, which is also called as the
drainage area of the river.
Out-flowing
Rivers refer to rivers directly or indirectly flowing into the sea. The area providing
water to the out-flowing rivers is called as out-flowing area.
Inland Rivers refer to rivers in inland dry areas that die away in desert on the way or
infuse into inland lakes. The area providing water to the inland rivers is
called as inland area.
Mineral
Resources refer to useful minerals, with solid state, liquid state, gaseity,
due to the geological process. Minerals are important natural resources, and
important material base for social development. At present, there are more than
170 types of minerals discovered in
Ensured
Mineral Reserves refer to the actual mineral reserves, which equal to the proven mineral
reserves (including industrial reserves and prospective reserves) minus
extracted parts and underground losses.
Average
Temperature refers to the air temperature.
Monthly average temperature is the summation of
average daily temperature of one month divided by the actual days of that
particular month.
Annual average temperature is the summation of
monthly average of a year divided by 12 months.
Average
Annual Relative Humidity refers to the ratio of actual water vapour pressure to
the saturation water vapour pressure under the
current temperature. The calculation method is the same as that of temperature.
Volume
of Precipitation refers to the deepness of liquid state or solid state (thawed) water falling
from the sky to the ground that has not been evaporated, infiltrated or run
off. The calculation method is as follows:
Monthly precipitation is the summation of daily
precipitation of a month.
Annual precipitation is the summation of 12 months
precipitation of a year.
Annual
Sunshine Hours refer to the actual hours of sun irradiating the earth, usually expressed in hours.
The calculation method is the same as that of the precipitation.
Total Water Resources refers to total volume of surface water and groundwater
and is measured as run-off for surface water and replenishment of groundwater
with rainfall in local area.
Surface Water Resources refers to total volume of year by year renewable dynamic
resources which exist in rivers, lakes, glaciers and other surface water and
are the natural run-off of rivers.
Groundwater Resources refers to total volume of year by
year renewable dynamic resources which exist in saturation acquifers
of groundwater and are measured as replenishment of groundwater with rainfall
and surface water.
Duplicated Measurement between Surface Water and Groundwater refers to mutual exchange between surface water and
groundwater, i.e. run-off of rivers includes some depletion into groundwater
while groundwater includes some replenishment from surface water.
Water Supply refers to gross water of various sources supplied to consumers,
including losses during distribution.
Surface Water Supply refers to withdrawals by surface water supply system,
broken down with storage, flow, pumping and transfer. Supply from storage
projects includes withdrawals from reservoirs; supply from flow includes
withdrawals from rivers and lakes with natural flows no matter if there are
locks or not; supply from pumping projects includes withdrawals from rivers or
lakes with pumping stations; and supply from transfer refers to water supplies
transferred from first-level regions of water resources or independent river
drainage areas to others, and should not be covered under supplies of storage,
flow and pumping.
Groundwater Supply refers to withdrawals from supplying wells, broken down
with shallow layer freshwater, deep layer freshwater and slightly brackish
water. Groundwater supply for urban areas includes water mining by both
waterworks and own wells of enterprises.
Other Water Supply Sources include supplies by waste-water treatment, rain collection,
seawater desalinization and other water projects.
Water Use refers to gross water used by various water users,
including losses during distribution.
Water Use by Agriculture includes uses of water by irrigation of farming fields,
forestry and orchards, irrigation of grassland, replenishment of fishing farms
and water used by animal husbandry.
Water Use by Industry refers to new withdrawals of water, excluding reuse of
water within enterprises.
Water Use by Living Consumption includes use of water for living consumption in both urban
and rural areas. Urban water use by living consumption is composed of household
use and public use (including tertiary industry and construction). Rural water
use by living consumption includes water used by households.
Water Use by Ecological and Environmental Protection includes replenishment of rivers and lakes and use for
urban environment.
Common
Industrial Solid Wastes Produced refers to the industrial solid wastes
that are not listed in the 《National Catalogue of Hazardous Wastes》, or not regarded as hazardous according to the national hazardous waste
identification standards (GB5085), solid waste-Extraction procedure for
leaching toxicity (GB5086) and solid waste-Extraction procedure for leaching
toxicity (GB/T 15555). The calculation formula is as followed:
Common Industrial Solid Wastes Produced = (common
industrial solid wastes utilized – the proportion of utilized stock of previous
years) + common industrial solid waste stock + (common industrial solid wastes
disposed – the proportion of disposed stock of previous years) + common
industrial solid wastes discharged.
Common
Industrial Solid Wastes Comprehensively Utilized refers to volume of solid wastes from which useful materials can be extracted or
which can be converted into usable resources, energy or other materials by
means of reclamation, processing, recycling and exchange (including utilizing
in the year the stocks of industrial solid wastes of the previous year) during
the report period, e.g. being used as agricultural fertilizers, building
materials or as material for paving road. Examples of such utilizations include
fertilizers, building materials and road materials. The information shall be
collected by the producing units of the wastes.
Common Industrial
Solid Wastes Disposed refers to the quantity of industrial
solid wastes which are burnt or specially disposed using other methods to alter
the physical, chemical and biological properties and thus to reduce or
eliminate the hazard, or placed ultimately in the sites meeting the
requirements for environmental protection during the report period.
Stock
of Common Industrial Solid Wastes refers to the volume of solid wastes placed in special facilities or special
sites by enterprises for purposes of utilization or disposal during the report
period. The sites or facilities should take measures against dispersion, loss,
seepage, and air and water contamination.
Common
Industrial Solid Wastes Discharged refers to the volume of industrial solid wastes dumped or discharged by
producing enterprises to disposal facilities or to other sites.
Hazardous
Wastes Produced refers to the
volume of actual hazardous wastes produced by surveyed samples throughout the
year of the survey. Hazardous waste refers to those included in the national
hazardous wastes catalogue or specified as any one of the following properties
in light of the national hazardous wastes identification standards and methods:
explosive, ignitable, oxidizable, toxic, corrosive or
liable to cause infectious diseases or lead to other dangers. The report of
this indicator should follow the 《National Catalogue of Hazardous Wastes》 (the NO.1 Ministry Order in 2008 by the Ministry of Environment
Protection and National Development and Reform Commission).
Hazardous
Wastes Utilized refers to the
volume of hazardous wastes that are used to extract materials for raw materials
or fuel throughout the year of the survey, including those utilized by the
producing enterprise and those provided to other enterprises for utilization.
Hazardous
Wastes Disposed refers to the quantity of hazardous wastes which are burnt or specially
disposed using other methods to alter the physical, chemical and biological
properties and thus to reduce or eliminate the hazard, or placed ultimately in
the sites meeting the requirements for environmental protection during the
report period.
Stock
of Hazardous Wastes refers to the volume of hazardous wastes specially packaged and placed in
special facilities or special sites by enterprises. The special stock
facilities should meet the
requirements set in relevant environment protection laws and regulations such
as “Pollution Control Standards for Hazardous Waste Stock” (GB18597-2001) in regard
to package of hazardous waste, location, design, safety, monitoring and
shutdown, and take measures against dispersion, loss, seepage, and air and
water contamination.
Consumption
Wastes Transported refers to volume of consumption wastes collected and
transported to disposal factories or sites during the reference period.
Consumption wastes are solid wastes produced from urban households or from
service activities for urban households, and solid wastes regarded by laws and
regulations as urban consumption wastes, including those from households,
commercial activities, markets, cleaning of streets, public sites, offices,
schools, factories, mining units and other sources.
Ratio of
Consumption Wastes Treated refers to consumption wastes treated over that produced.
In practical statistics, as it is difficult to estimate, the volume of
consumption wastes produced is replaced with that transported. It is calculated
as:
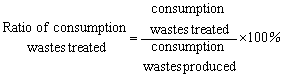
Forest
Area refers
to the area of trees and bamboo grow with a canopy density above 0.2 degree, the
area of shrubby tree according to regulations of the government, the area of
forest land inside farm land and the area of trees planted by the side of
villages, farm houses and along roads and rivers.
Area of Man-made Forests refer to the area of stable growing
forests, planted manually or by airplanes, with a survival rate of 80% or
higher of the designed number of trees per hectare, or with a canopy density of
0.20 degree or above after 3-5
years of manual planting or 5-7 years of airplane planting.
![]()
Total Standing
Stock Volume
refers to the total stock volume of trees growing in land, including
trees in forest, trees in sparse forest, scattered trees and trees planted by
the side of villages, farm houses and along roads and rivers.
Stock
Volume of Forest refers to total stock volume of wood growing in forest area, which shows the
total size and level of forest resources of a country or a region.
Area of Afforestation refers to the total area of land suitable for afforestation, including barren hills, idle land, sand
dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland and “grain for green” land, on which
acres of forests, trees and shrubs are planted through manual planting.
Manual Planting refers to technical measures of sowing, planting
seedlings and divided transplanting on land suitable for afforestation,
including barren hills, idle land, sand dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland
and “grain for green” land to increase vegetation coverage rate of forests.
Airplane
Planting refers to technical measures of airplane
planting with of appropriate artificial help taken under the influence of
natural power to restore certain amount of seedlings on land suitable for afforestation, including barren hills, idle land, sand
dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland and “grain for green” land, with an aim
of increasing vegetation coverage rate of forests.
No-stocked
Land and Sparse Forest Land Newly Closed for Afforestation
This Year refers to the area of sparse forest land, brush shrub land, stump land, burned
land, barren hills, barren land, sand dunes where trees can naturally grow or
sprout, which are demarcated, closed down and returned to forest, shrubbery and
grass land with the assistance of special measures by men.
Timber Forests refer to forests which are mainly for the production of
timber, including bamboo groves planted to harvest bamboos.
By-product Forests refer to forests that mainly produce fruits, nuts,
edible oil, beverages, indigents, raw materials and medicine materials.
By-product forests are planted to harvest the fruits, leaves, bark or liquid of
trees, and consume them as food or raw materials for the manufacturing
industry, such as tea-oil trees, tung oil trees,
walnut trees, camphor trees, tea bushes, mulberry trees, fruit trees, etc.
Protection Forests refer to forests, trees and bushes planted mainly for
protection or preservation purpose, including water resource conservation
forests, water and soil conservation forests, windbreak and dune-fixing
forests, farmland and pasture protection forests, riverside protection forests,
roadside protection forests, etc.
Fuel Forests refer to forests planted mainly for fuels.
Forests for Special Purpose refer
to forests planted mainly for national defence, environment protection or
scientific experiments, including national defence forests, experimental
forests, mother-tree forests, environment protection forests, scenery forests,
trees in historical or scenic spots, forests in natural reserves.
Wetlands refer to marshland and peat bog, whether natural or man-made,
permanent or temporary; water covered areas, whether stagnant or flowing, with
fresh or semi-fresh or salty water that is less than 6 meters deep at low tide;
as well as coral beach, weed beach, mud beach, mangrove, river outlet, rivers,
fresh-water marshland, marshland forests, lakes, salty bog and salt lakes along
the coastal areas.
Natural Reserves refer to
number of certain areas of land, or waters that have been set aside and put
under special protection and management in order to protect natural environment
and natural resources, and promote the sustainable development of national
economy. They are subject to formal approval from governments of various
levels. According to the protected targets, natural reserves can be divided
into three categories: reserves of natural ecological system, natural reserves
of wildlife species, and natural heritage of historical significance.Scenic spots and cultural preservation zones are
not included.
Landslides refer to the geological phenomenon of unstable rocks
and earth on slopes sliding down along certain soft surface as a result of
gravitational force.
Collapse
refers to the
geological phenomenon of large mass of rocks or earth suddenly collapsing from
the mountain or cliff as a result of gravitational force.
Mud-rock Flow refers to the sudden rush of flood torrents
containing large amount of mud and rocks in mountainous areas.
Land Subside refers to the geological phenomenon of surface rocks or earth
subsiding into holes or pits as a result of natural or human factors.
Number
of Forest Fires refers to the
number of fires in forests, woods and woodland outside of the downtown areas of
cities. In light of the area plagued by fires and the number of casualties,
forest fires can be categorized into usual forest fires, relatively larger
fires, serious forest fires and extraordinary serous forest fires: 1). Usual
forest fires: the destructed forest area is less than 1 hectare, or the fire
erupts in other woodland, or the number of deaths is no less than 1 but less
than 3, or the number of seriously injured persons is no less than 1 but less
than 10 persons. 2). Relatively larger forest fires: the destructed forest area
is no less than 1 hectare but less than 100 hectares, or the number of deaths
is no less than 3 but less than 10, or the number of seriously injured persons
is no less than 10 but less than 50 persons. 3). Serious forest fires: the
destructed forest area is no less than 100 hectares but less than 1000
hectares, or the number of deaths is no less than 10 but less than 30, or the
number of seriously injured persons is no less than 50 but u less than 100
persons. 4). Extraordinary serious forest fires: the destructed forest area is
no less than 1000 hectares, or the number of deaths is no less than 30, or the
number of seriously injured persons is no less than 100 persons.
Forest
Harmful Organisms refer to the diseases, pests,rats and harmful plants that plague forests,wood, desert and wetland vegetation.
Environmental
Emergencies refer to environmental
emergencies that caused or likely to cause significant causalities, serious
property damages and pose a major threat and damage to the economic, social or
political stability of the country or a region, or have significant social
impact that related to the public safety.
Number
of Earthquakes the number of earthquakes of all magnitude that cause damages (including
casualties or economic losses).