Explanatory
Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Regular
Institutions of Higher Education refer to
educational establishments recruiting graduates from senior secondary schools
as the main target through National Matriculation TEST. They include full-time universities, independently established colleges,
colleges, and institutions of higher professional education, institutions of
higher vocational education and others.
Universities and independently established colleges
primarily provide undergraduate and above courses; colleges mainly impart
undergraduate courses, institutions of higher professional education and
institutions of higher vocational education primarily provide professional
trainings; and others refer to educational establishments, which are
responsible for enrolling higher education students under the State Plan but
not enumerated in the total number of schools, including: branch schools of
universities and colleges and junior colleges.
Institutions of Higher Education for Adults refer to educational establishments, enrolling personnel with senior
secondary school or equivalent education through National Matriculation
TEST for Adult, and providing higher education
courses in forms of correspondence, spare time, or full time for adults.
Institutions of higher learning for adults include schools of higher education
for staff and workers, schools of higher education for peasants, colleges for
management cadres, pedagogical colleges, independent correspondence colleges, radio
and television universities and other educational establishments. Other
educational establishments refer undertakings to enrol adult students but not
enumerated in the number of schools under the State Plan.
Net Enrolment Ratio of Primary Schools refers to the proportion of school age children enrolled at schools to
the total number of school age children both in and outside schools (including
retarded children, but excluding blind, deaf and mute children). The formula
is:
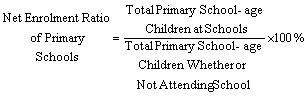
Government Appropriation for
Education refers to the public budgetary fund
for education, taxes and fees collected by governments at all levels that are
used for education purpose, enterprise appropriation for enterprise-run
schools, income from school-run enterprises and social services that are used
for education purpose and other national appropriations for education.
Public Budgetary Fund for Education refers to education funding from the central and local financial
departments and supervision departments that is planned to be allocated to
various schools, education administration institutions and education
institutions within the reference year, which is within the State budgetary
expenditure, including: appropriated funds for education, science and research,
capital construction and others.
Research and Development (R&D) refers to systematic and creative activities in the field of science
and technology aiming at increasing the knowledge and using the knowledge for
new application. R&D includes 3 categories of activities: basic research,
applied research and experimentation for development. The scale and intensity
of R&D are widely used internationally to reflect the strength of S&T
and the core competitiveness of a country in the world.
Basic Research refers to empirical or theoretical research aiming at obtaining new
knowledge on the fundamental principles regarding phenomena or observable facts
to reveal the intrinsic nature and underlying laws and to acquire new
discoveries or new theories. Basic research takes no specific or designated
application as the aim of the research. Results of basic research are mainly
released or disseminated in the form of scientific papers or monographs. This
indicator reflects the innovation capacity for original knowledge.
Applied Research refers to creative research aiming at obtaining new knowledge on a
specific objective or target. Purpose of the applied research is to identify
the possible uses of results from basic research, or to explore new
(fundamental) methods or new approaches. Results of applied research are expressed
in the form of scientific papers, monographs, fundamental models or invention
patents. This indicator reflects the exploration of ways to apply the results
of basic research.
Experiments and Development refer to systematic activities aiming at using the knowledge from basic
and applied researches or from practical experience to develop new products,
materials and equipment, to establish new production process, systems and
services, or to make substantial improvement on the existing products, process
or services. Results of experiment and development activities are embodied in
patents, exclusive technology, and monotype of new products or equipment. In
social sciences, experiment and development activities refer to the process of
converting the knowledge from basic or applied researches into feasible
programmes (including conduct of demonstration projects for assessment and
evaluation). There are no experiment and development activities in the science
of humanities. This indicator reflects the capability of transferring the
results of S&T into technique and products, and measures the realization of
S&T in spearheading the economic and social development.
R
& D Personnel refer to persons engaged in research, management and supporting activities of
R & D, including persons in the project teams, persons engaged in the
management of S&T activities of enterprises and supporting staff providing
direct service to the research projects. This indicator reflects the size of
personnel engaged in R&D activities with independent intellectual property.
Full-time Equivalent of R&D
Personnel refers to the sum of the full-time
persons and the full-time equivalent of part-time persons converted by
workload. For instance, if there are 2 full-time persons and 3 part-time workers
(20%, 30% and 70% of working hours respectively on R&D activities), the
full-time equivalent are 2+0.2+0.3+0.7=3.2 person-years. This is an
internationally comparable indicator of S&T manpower input.
Total Expenditure of Funds on R&D
refers to the real
expenditure of surveyed units on their own R&D activities (basic research,
application study, test and development) including direct expenditure on
R&D activities, indirect expenditure of management and services on R&D
activities, expenditure on capital construction and material processing by
others. Excluding the expenditure on production activities, return of loan, and
fees transferred to cooperated and entrusted agencies on R&D activities.
Expenditure of Government Funds on
R&D refers to
the expenditure of funds on R&D activities from government agencies at
different levels, including appropriate funds on science and technology from
financial departments, scientific funds, operating expenses from education
departments and the real expenditure of extra budgetary funds from government
agencies.
Expenditure of Funds of Enterprises
on R&D refers to
the expenditure of funds on R&D activities from self-raised funds of
enterprises and funds from other enterprises through entrustment, and the
expenditure of funds of institutions, such as institution of scientific
research and universities, from enterprises.
Number of R&D Projects (subjects)
refers to the number of
R&D projects (subjects) set up and implemented at the reference year, and
the number of R&D projects (subjects) set up in former years and under
implementation, including the projects (subjects) finished and failed at the
reference year, excluding the projects (subjects) implemented by others through
entrustment.
Full-time Equivalent of R&D
Personnel refers to the full-time equivalent
of persons actually engaged in R&D projects (subjects).
Expenditure of Funds on R&D
Projects (subjects) refers to
the real expenditure of internal funds of the surveyed units on research and
test of R&D projects (subjects) at the reference year, including service
fee, other daily expenditure, cost for capital goods, cost of external process;
excluding expenditure of funds transferred to other cooperated and entrusted
units of the projects.
Sales
Income of New Products refers to the sales income of
new products of the enterprises at the reference period. New products refer to products developed
and produced with new technologies and designs or improved in structure, material,
process and other aspects so that their performance are improved or their
functions expanded. New products include those affirmed by government
authorities in their validity period and also those developed by enterprises
without the affirmation of government authorities within one year after they
are put into production.
Patent is
an abbreviation for the patent right and refers to the exclusive right of
ownership by the inventors or designers for the creation or inventions, given
from the patent offices after due process of assessment and approval in
accordance with the Patent Law. Patents are granted for inventions, utility
models and designs. This indicator reflects the achievements of S&T and
design with independent intellectual property.
Patented Inventions refer to new technical proposals to the products or methods or their
modifications. This is universal core indicator reflecting the technologies
with independent intellectual property.
Patented Utility Models refer to the practical and new technical proposals on the shape and
structure of the product or the combination of both. This indicator reflects
the condition of technological results with certain technical content.
Designs
refer to the aesthetics and industrially applicable new designs for the shape,
pattern and colour of the product, or their combinations. This indicator
reflects the appearance design achievements with independent intellectual
property.