Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
Medical
and Health Care Institutions refer to the units which have been
qualified the Certification of Health Care Institution by the administration of
public health, or qualified the Certification of Corporate Unit by the civil
affairs, administration for industry and commerce, commission office for public
sector reform, and engaging in medical care, disease prevention and control,
health supervision and inspection, medicine research and on-job training, etc.,
including: hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized
public health institutions, and other medical and health care institutions.
Hospitals include general hospitals, hospitals specialized in traditional
Chinese medicine, hospitals of integrated traditional Chinese and western
medicine, nationalities hospitals, specialized hospitals and nursing hospitals.
Health
Care Institutions at Grass-root Level include
community health service centers, urban health centers, township health
centers, village clinics, outpatient departments and clinics (health centers).
Specialized
Public Health Institutions include centers for
disease control and prevention, specialized disease prevention and treatment
institutions, women and children care agencies, health education institutions,
first aid centers, blood gathering and supplying institutions, health
supervision and inspection agencies, and family planning technical service
centers supervised by health institutions.
Other
Medical and Health Care Institutions include
sanatoriums, clinical laboratory centers, medicinal scientific research
institutions, on-job training institutions, medical examination centers, rural
water improvement centers, talent exchange centers, and statistical information
centers, etc.
Health
Care Employees refer to all employees engaged in the health care institutions, such as
hospitals, health care institutions at grass-root level, specialized public
health institutions, and other medical and health care institutions, including
medical technical personnel, village doctors and assistants, other technical
personnel, managerial and service staff.
Medical
Technical Personnel refer to the professional staff engaged
in health care, including licensed doctors, licensed assistant doctors,
registered nurses, pharmacists, laboratory technicians, imaging staff, health
care supervisors and intern doctors, pharmacists, nurses, and technical
personnel, excluding the medical technical personnel engaged in managerial job.
Licensed
Doctors
refer to the medical workers who have obtained the licenses of qualified
doctors and are employed in medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare
institutions, excluding the licensed doctors engaged in management job. The
licensed doctors are divided into 4 categories: clinician, Chinese medicine
physicians, dentist and public health physicians.
Licensed
Assistant Doctors refer to the medical workers who
have obtained the licenses of qualified assistant doctors and are employed in
medical treatment, disease prevention or healthcare institutions, excluding the
licensed assistant doctors engaged in management job. The classification of
licensed assistant doctors is clinician, Chinese medicine, dentist and public
health.
Number
of Licensed (Assistant) Doctors per 10000 Population The formula is:
Number of Licensed Doctors per 10000
Population = (Number of Licensed Doctors + Number of Licensed Assistant
Doctors) / Population *10000
The population is the figure of household
registration from the Ministry of Public Security.
Number
of Medical Technical Personnel per 10000 Population The formula is:
Number of Medical Technical Personnel per
10000 Population = Number of Medical Technical Personnel / Population *10000
The population is the figure of household
registration from the Ministry of Public Security.
Number
of Beds of Medical and Health Care Institutions per 10000 Population the formula is:
Number of Beds of Medical and Health Care
Institutions per 10000 Population = Number of Beds of Medical and Health Care
Institutions / Population *10000
The population is the figure of household
registration from the Ministry of Public Security.
Incidence
Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the incidence cases notifiable class A
and class B infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference
region in the reference year. The formula is:
Incidence Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases = Incidence Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases /
Population *100000
Death
Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the death cases notifiable class A and
class B infectious diseases per 100 thousand population in the reference region
in the reference year. The formula is:
Death Rate of A and B Type of Notifiable Infectious Diseases= Death Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases /
Population *100000
Mortality
Rate of A and B Type Notifiable Infectious Diseases refer to the ratio of death cases notifiable
class A and class B infectious diseases to the incidence cases in the reference
region in the reference year. The formula is:
Mortality Rate of A and B Type Notifiable Infectious Diseases = Death Cases Notifiable Class A and Class B Infectious Diseases /
Incidence Cases *100%
Crude
Mortality Rate refers to the ratio of deaths to the average population in a year of the
region, and usually is presented by ‰.
Standardized
Mortality Rate refers to the mortality rate at
reference age calculated according to the age structure of a group of
population.
Fatality
Rate refers to the ratio of deaths caused by a
disease to the population infected by it in a give period (generally one year),
and usually is presented by %.
Maternal
Mortality Rate refers to number of maternal death
per 10,000 maternal. Generally refers to maternal mortality from pregnancy to
42 days after parturition due to pregnancy or any treatment of pregnancy,
however, accidental deaths are not included. According to internationally
accepted calculation method, the live births are used to represent the total
number of maternal.
Number
of Live Births refers to the number of newborn
having one of four indicators like heartbeat, breathing, umbilical cord
pulsation and involuntary muscle contraction after childbirth with gestation of
at least 28 weeks or above (if the gestation is not clear, then refer to the
birth weight of 1000 grams and above).
Mortality
Rate of Children under 5 refers to the ratio of deaths of children under
Newborn
Mortality Rate refers to the ratio of neonatal deaths in a year to the number of live
births, and usually is presented by ‰. Neonatal deaths refer to the deaths of
new-birth under the age of 28 days (0-27 days).
Number
of Persons Participated in the New Rural Cooperative Medical System refers to the number of persons who have given payment to the new
cooperative medical system by the deadline of fundraising during the year
according to the implementation plan of the new system.
Expenditure
of Funds for the New Rural Cooperative Medical System This Year refers to expenditures on compensation funds for the new rural cooperative
medical system from the fund account of new cooperative medical system this
year.
Persons
Benefited from the Compensation Expenditure of New Rural Cooperative Medical
System
refers to the number of persons participated in the new system who have
been compensated for medical treatment in the year, including hospitalization,
family account form, out-patient, large special diseases out-patient, normal
childbirth in hospital, medical examination and other compensations
Funds
Raised for the New Rural Cooperative Medical System this Year refers to the amount of funds raised this year and put into the special
new rural cooperative medical account, including the matching funds of central
and local governments, paid money by farmers (including relief funds paid by
the civil affairs department and other relevant departments), all the interest
income generated this year of the funds and funds actually raised from other
channels this year. The amount of funding equals to the funds entering into the
special new rural cooperative medical account, excluding the carry-over funds
from the previous year.
Total
Expenditure on Public Health
refers to the total expenditure on medical and health care services of a
country or a region in a certain period of time (usually a year) in monetary
form. The accounting result and its basic data not only provide macro-economic
information for adjusting and making of health policies of government, but also
important basis for evaluating the importance given by the whole society
on human health, and
analyzing the fairness and efficiency of the health care system.
Government
Expenditure on Public Health refers to the expenditure of the governments at all levels on medical and
health care services, medical subsidies, health administration and health
insurance management, and undertakings of family planning etc.
Social
Expenditure on Public Health refers to all inputs of society except
the government in public health including the expenditures on social medical
security, commercial health insurance,
private expenditure on operation of medical and health care, social
donation and contribution, and income from administrative fees etc.
Individual
Cash Expenditure on Health refers to expenditure in cash on various health services by rural and
urban residents, including self payments of residents within the system of
multi-medical insurance.
Average
Expenditure on Health refers to the ratio of total
expenditure on health in a year to the average population.
Ratio
of Total Expenditure on Public Health to GDP refers
to the ratio of total expenditure on public health in a year to GDP, which
indicates the support given by a nation to health work, the capital inputs of
the whole society in the public health, and the attention paid on the health of
residents in certain period of time and under certain economic conditions.
Serviceman
Recreation Habitation also called retired
servicemen recreation habitation, refers to the units
which are administrated by departments of civil affairs with independent
accounting and provide services to the retired servicemen.
Military
Supply Stations also called units of management of
military supply. They are the general name of units such as military food
supply stations, military water supply stations, servicemen transfer reception
stations, which are managed by departments of civil affairs entrusted by local
governments with independent accounting, and provide services to army during
the war or peacetime.
Licensed
Social Workers refer to those who passed the
National Aptitude Test for Social Workers and obtained the certificates.
Social
Service Beds per Thousand Population The formula is:
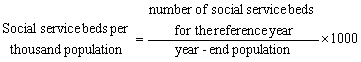
Social
Welfare Enterprises refers to those
welfare-oriented enterprises employing a significant number of handicapped
people with certain labour ability (handicapped
employees shall exceed 10% of the production staff), including welfare
factories, artificial limb plants as well as other welfare enterprises.
Number
of Orphans refers to juveniles under age of 18 that have lost parents or can't find
parents. Orphans are affirmed by department of civil affairs at county level
according to relevant regulations.
Number
of Adoption Registration of Family Children refers to abandoned babies that can’t find parents, children and orphans
raised by welfare institutions adopted by Chinese citizens, or children adopted
by foreign nationals, which have registered in department of civil affairs at
county level and above, and gained legal adoption right. One registration means
one case.
Adoption
Registration of Chinese Citizens refers to adoption registration of children by Chinese citizens, which
include persons from
Adoption
Registration of Foreign Nationals refers to adoption registration of children by foreign nationals, which
include stateless persons, or adoption by couples with foreign nationals for
one party.
Number
of Urban Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those whose average family income is below
a minimum local standard by the end of the reporting period, including both the
employed and unemployed, laid off and retired, and those jobless people without
stable residence or valid IDs.
Number
of Rural Residents Entitled to Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those receiving the minimum living
allowances from the local government or community in the rural areas where this
allowances system is in place as of the end of the reference period.
Households
Enjoying Five Guarantees refers to those senior
citizens, handicapped or under-aged who, without labour
ability, can not make a living by themselves and whose statutory providers are
unable to support them or who have no statutory providers at all.
Number
of Rural Recipients of Traditional Relief refers to
the poor people entitled to traditional relief in rural areas where the minimum
living allowances system is not in place.
Number
of Service Facilities in Communities refers to the
number of non-profit welfare facilities set up for community residents’ in
particular the community-based centers that serve senior citizens, the
handicapped or children, recreational centers, service centers, nursing homes,
apartments for the elderly (nursery for the aged), work and treatment stations
for the handicapped, day-care centers for handicapped children, domestic help
agencies and dating services, as well as social insurance management agencies
for the employees. Different types of community service providers that share
the same premise are regarded as one community service facility. The
requirements for a social service facility of communities include: (1)
independent accounting; (2) fixed employees; (3) provision of certain services;
and (4) with certain places.
Coverage
Rate of Service Facilities in Communities The formula is:
Coverage rate of service facilities in
communities = number of service facilities in communities/number of village
committees + communities×100%
Crude
Divorce Rate refers to ratio of divorced couples to
the annual average population for the reference year, the formula is:
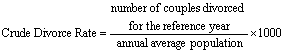 ‰
‰
Supervision
Rate refers to the percentage of patients among the
total number of registered mental disease patients, who participate in social
integrated and open treatment and rehabilitation programmes
through various forms such as supervision groups, family treatment, employment
or guidance from psychiatric institutions. This indicator reflects the
implementation of various measures aimed at rehabilitating those mental
patients.
Social
Participation Rate refers to proportion of mental disease patients who are able to manage
their daily life and participate in economic activities to the total number of
mental disease patients under supervision. This indicator reflects the
condition of recovery of those mental patients and their participation in
social activities.
Violent
Events Rate refers to the number of the patients
with mental diseases who have violated the Public Security Regulations as a
percentage of the total registered patients with mental diseases within the
year.
Handicapped
School-age Children without School Attendance
refers to the number of handicapped children of the school age as prescribed by
the provincial government in accordance with the Law on Compulsory Education who fail to attend any schools for
various reasons as of December 31 of the current year.
Centralized
Employment refers to the number of the urban
handicapped residents employed, in a centralized manner, by welfare
enterprises, work and treatment agencies, blind massagists’
centers and other organizations as of December 31of the current year.
Proportionate
Employment refers to the number of the urban
handicapped residents employed by governmental bodies, organizations, corporate
and public institutions, and various economic organizations in a decentralized
manner as of December 31 of the current year.