Territory refers to territorial land, sea
and air space under the administration of the People’s Republic of
Climate refers to the natural environmental
status formed by the long-term exchange of energy and mass between the earth
and the atmosphere, and is the result of interaction of many factors. Climate
is both one of the environment factors and also the important resources for
living and production activities of the human being. The average values across
several years of meteorological factors such as temperature, rainfall and
humidity are used as important parameters to describe the climate of a region,
while the average values (or total values) of a given year or month of
meteorological factors reflect the key characteristics of climate for that
period of time.
Natural Resources refer to material resources that could
be obtained from the nature by human being and used for production and living. Natural
resources in general can be classified as renewable resources and non-renewable
resources. Renewable resources refer to resources that could be renewed and
recycled during a relatively short period of time, including land resource,
water resource, climate resource, biology resource and marine resource.
Non-renewable resources include resources that could not be renewed, such as
minerals and geothermal resource.
Area of Cultivated Land refers to area of land reclaimed for the
regular cultivation of various farm crops, including crop-cover land, fallow,
newly reclaimed land and land laid idle for less than 3 years.
Area of Afforested Land refers to area for land for trees
bamboo, bushes and mangrove, including forest-covered land, bush-covered land,
sparse forest land, land planned for afforestation
and nurseries of young trees.
Area of Grassland refers to area of grassland,
grass-slopes and grass-covered hills with a vegetation-covering rate of over 5%
that are used for animal husbandry or harvesting of grass. It includes natural,
cultivated and improved grassland areas.
Inland Water Area refers to water area of rivers, lakes,
ponds, reservoir, etc.
Ocean is the general name for sea and
ocean. Ocean refers to the main body of large salt water connected with the
earth. Sea refers to the edge areas of the salt water on the earth that are
compartmentalized or surrounded by land, island, reef or peninsula.
Marine Cultivatable Areas refer to water areas in beach, shallow
sea and lough that are used to breed marine cash
propagation, such as fish, shrimp, crab, shellfish, alga and so on.
Runoff refers to the water gathered at the way
out of the cross section of drainage area either from the surface or
underground after deducting the wastage of the precipitation on the land.
Runoff can be divided into surface runoff, underground runoff and within soil
runoff. Surface runoff refers to water flowing to the rivers, lakes, swamps,
and seas on the surface of the earth. Underground runoff refers to water flow
to rivers, lakes, swamps, and seas through the water-bearing stratum of
confined layer or unconfined layer.
Volume of Runoff refers to the total volume of water
running through a certain cross section of a river during a certain period of
time, reflecting the water resource condition in a country or a region. The
formula for calculating volume of runoff is as follows:
Runoff =Precipitation-Evaporation
Drainage Area Each river has its own main stream and
branches to form the water system of the river. Each river has its own
catchment’s area, which is also called as the drainage area of the river.
Out-flowing Rivers refer to rivers directly or indirectly
flowing into the sea. The area providing water to the out-flowing rivers is
called as out-flowing area.
Inland Rivers refer to rivers in inland dry areas that
die away in desert on the way or infuse into inland lakes. The area providing
water to the inland rivers is called as inland area.
Continental Shelf refers to seabed and subsoil of sea
floor area that is beyond the marginal sea of the coastal countries which
stretches naturally of its land territory to continent edge, and its width is
defined by the United Nations Marine Convention. The continental shelf area is
rich in aquatic products, and its seabed contains petroleum, natural gas and
other mineral resources, which belong to the coastal countries. The continental
shelf of our country is the natural stretch of its land territory to the
continent edge besides the marginal sea of our country. It extends to the
seabed and subsoil of the sea floor area to the edge of the continent. If the
distance from the baseline of the marginal sea to the continent edge is less
than 200 nautical miles, it can be extended to 200 nautical miles.
Shallow Sea Cultivation refers to the breeding of marine cash
propagation in the cultivatable shallow sea.
Sea-beaches Cultivation refers to the breeding of marine
propagation in sea-beaches which are made possible by levelling-off
the ooze or mud in the tideland and banking up dams.
Harbour Cultivation refers to marine cultivation conducted
in harbours, bays, or the sea-beaches or marshes
around seaside and bayou by blocking the gate and banking up the dam.
Mineral Resources refer to useful minerals, with solid
state, liquid state, gaseity, due to the geological
process. Minerals are important natural resources, and important material base
for social development. At present, there are more than 170 types of minerals
discovered in
Ensured Mineral Reserves refer to the actual mineral reserves,
which equal to the proven mineral reserves (including industrial reserves and
prospective reserves) minus extracted parts and underground losses.
Temperature refers to the air temperature. China
uses centigrade as the unit. The thermometry used for weather observation is
put in a breezy shutter, which is 1.5 meters high from the ground. Therefore,
the commonly used temperature refers to the temperature in the breezy shutter
1.5 meters away from the ground. The calculation method is as follows:
Monthly average temperature is the summation of average daily temperature
of one month divided by the actual days of that particular month.
Annual average temperature is the summation of monthly average of a year
divided by 12 months.
Relative Humidity refers to the ratio of actual water vapour pressure to the saturation water vapour
density under the current temperature. The calculation method is the same as
that of temperature.
Volume of Precipitation refers to the deepness of liquid state
or solid state (thawed) water falling from the sky to the ground that has not
been evaporated, infiltrated or run off. The calculation method is as follows:
Monthly precipitation is the summation of daily precipitation of a month.
Annual precipitation is the summation of 12 months precipitation of a
year.
Sunshine Hours refer to the actual hours of sun
irradiating the earth. The calculation method is the same as that of the
precipitation.
Total Water Resources refers to total volume of water resources measured as run-off for
surface water from rainfall and recharge for groundwater in a given area,
excluding transit water.
Surface Water Resources refers to total renewable
resources which exist in rivers, lakes, glaciers and other collectors from
rainfall and are measured as run-off of rivers.
Groundwater Resources refers to replenishment of
aquifers with rainfall and surface water.
Duplicated Measurement between Surface Water and Groundwater refers to mutual exchange
between surface water and groundwater, i.e. run-off of rivers includes some
depletion into groundwater while groundwater includes some replenishment from
surface water.
Water Supply refers to gross water supply by
supply systems from sources to consumers, including losses during distribution.
Surface Water Supply refers to withdrawals by
surface water supply system, broken down with storage, flow, pumping and
transfer. Supply from storage projects includes withdrawals from reservoirs;
supply from flow includes withdrawals from rivers and lakes with natural flows
no matter if there are locks or not; supply from pumping projects includes
withdrawals from rivers or lakes with pumping stations; and supply from
transfer refers to water supplies transferred from first-level regions of water
resources or independent river drainage areas to others, and should not be
covered under supplies of storage, flow and pumping.
Groundwater Supply refers to withdrawals from
supplying wells, broken down with shallow layer freshwater, deep layer
freshwater and slightly brackish water. Groundwater supply for urban areas
includes water mining by both waterworks and own wells of enterprises.
Other Water Supply Sources include supplies by
waste-water treatment, rain collection, seawater desalinization and other water
projects.
Water Use refers to gross water use
distributed to users, including loss during transportation, broken down into
use by agriculture, industry, living consumption and ecological protection.
Water Use by Agriculture includes uses of water by
irrigation of farming fields and by forestry, animal husbandry and fishing.
Water use by forestry, animal husbandry and fishery includes irrigation of
forestry and orchards, irrigation of grassland and replenishment of fishing
farms.
Water Use by Industry refers to new withdrawals of
water, excluding reuse of water within enterprises.
Water Use by Living Consumption
includes use of water for living consumption in both urban and rural areas.
Urban water use by living consumption is composed of household use and public
use (including services, commerce, restaurants, cargo transportation, posts,
telecommunications and construction). Rural water use by living consumption
includes both households and animals.
Water Use by Ecological Protection
includes replenishment of rivers and lakes and use for urban environment.
Waste Water Discharged by Industry
refers to the volume of waste water discharged by industrial enterprises
through all their outlets, including waste water from production process,
directly cooled water, groundwater from mining wells which does not meet
discharge standards and sewage from households mixed with waste water produced
by industrial activities, but excluding indirectly cooled water discharged (It
should be included if the discharge is not separated from waste water).
Waste Water Directly Discharged into Sea refers to the volume of waste water directly discharged
into sea through outlets of enterprises situated by sea without going through
municipal sewerage networks or any other intermediates or being affected by any
other water bodies.
Industrial Waste Water Meeting Discharge Standards refers to volume of industrial waste water discharge which, with or
without treatment, reaches national or local standards with regard to all
pollutants.
Urban Non-industrial Waste Water
Discharge refers to annual discharge of
non-industrial waste water by urban households. It is estimated by per capita
coefficient using the formula:
![]()
![]()
Volume of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
Generated by Urban Non-industrial Waster Water refers to chemical oxygen demand
generated through the annual discharge of non-industrial waste water by urban
households. It is estimated as:
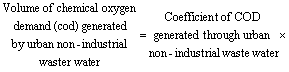

Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) refers
to the amount of oxygen required when chemical oxidants are used to oxidize
organic pollutants in water. A higher value of COD corresponds to more serious
pollution by organic pollutants.
Industrial Waste Air Emission
refers to the discharge into atmosphere of waste air containing pollutants
generated from fuel burning and production processes in enterprises within a
given period of time. It is calculated at standard status (273K, 101325Pa) as:
![]()
SO2 Emission through Non-industrial and Other Activities is calculated on the basis of consumption of coal by households and
other activities and the sulphur content of coal with the following formula:
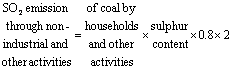
SO2 Emission through Industrial Activities refers to volume of sulphur dioxide emission from fuel burning and
production process by enterprises during a given period of time. It is
calculated as:
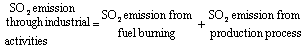
Industrial Soot Emission refers to the volume of soot
in smoke emitted in the process of fuel burning in the premises of enterprises.
Soot Emission by Consumption and Others
refers to the net volume of soot emitted by fuel burning from all social and
economic activities and operations of public facilities other than industrial
activities. It is calculated on the basis of coal consumption by households and
others.
Industrial Dust Emission refers to volume of dust
emitted by production process of enterprises and suspended in the air for a
given period of time, including dust from refractory material of iron and steel
works, dust from coke-screening systems and sintering machines of coke plants,
dust from lime kilns and dust from cement production in building material
enterprises, but excluding soot and dust emitted from power plants.
Industrial Solid Wastes Produced
refers to total volume of solid, semi-solid and high concentration liquid
residues produced by industrial enterprises from production process in a given
period of time, including hazardous wastes, slag, coal ash, gangue, tailings,
radioactive residues and other wastes, but excluding stones stripped or dug out
in mining - gangue and acid or alkaline stones not included (a stone is acid or
alkaline according to the pH value of the water being below 4 or above 10.5
when the stone is in, or soaked by water).
Hazardous Wastes refers to those included in
the national hazardous wastes catalogue or specified as any one of the
following properties in the national hazardous wastes identification standards:
explosive, ignitable, oxidizable, toxic, corrosive or
liable to cause infectious diseases or lead to other dangers.
Industrial Solid Wastes Utilized
refers to volume of solid wastes from which useful materials can be extracted
or which can be converted into usable resources, energy or other materials by
means of reclamation, processing, recycling and exchange (including utilizing
in the year the stocks of industrial solid wastes of the previous year).
Examples of such utilizations include fertilizers, building materials and road
materials. The information shall be collected by the producing units of the
wastes.
Rate of Utilization of Industrial Solid Wastes refers to the percentage of industrial solid wastes utilized over
industrial solid wastes produced (including stocks of the previous years). It
is calculated as:

Stock of Industrial Solid Wastes
refers to the volume of solid wastes placed in special facilities or special
sites for purposes of utilization or disposal. The sites or facilities should take
measures against dispersion, loss, seepage, and air and water contamination.
Industrial Solid Wastes Disposed
refers to the quantity of industrial solid wastes which are burnt or placed ultimately
in the sites meeting the requirements for environmental protection and not
salvaged or recycled (including disposition in the year of those wastes of
previous years). The disposition includes landfill (Safe landfills should be
conducted for hazardous wastes), incineration, containment spaces, deep
underground disposal, backfill in mining pits and disposal at sea.
Industrial Solid Wastes Discharged
refers to the volume of industrial solid wastes discharged by producing
enterprises to disposal facilities or to other sites. The wastes exclude stones
stripped or dug from mining (gangue and acid or alkaline waste stones not
included).
Output Value of Products Made from Waste Gas, Waste Water and Solid
Wastes refers to the current value of products with
waste gas, waste water and solid wastes as main materials of production.
Products sold and ready to sell shall be included while those produced for own
use shall not be included.
Consumption Wastes Transported
refers to volume of consumption wastes collected and transported to disposal
factories or sites. Consumption wastes are solid wastes produced from urban
households or from service activities for urban households, and solid wastes
regarded by laws and regulations as urban consumption wastes, including those
from households, commercial activities, markets, cleaning of streets, public
sites, offices, schools, factories, mining units and other sources.
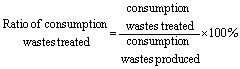
Ratio of Consumption Wastes Treated
refers to consumption wastes treated over that produced. In practical
statistics, as it is difficult to estimate, the volume of consumption wastes
produced is replaced with that transported. It is calculated as:
Area under Land Survey refers to
the total area of land, under the land survey, within the jurisdiction of the
administrative region, including land for agriculture use, land for
construction and unused land.
Land for Agriculture Use refers to land directly used for
agriculture production, including land for cultivation, gardening, forests, herbage
and other agriculture activities.
Forest Area refers to the area of forest where trees
and bamboo grow with canopy density above 0.2, including land of natural woods
and planted woods, but excluding bush land and thin forest land. It reflects
the total areas of afforestation.
Area of Man-made Forests refer to the area of
stable growing forests, planted manually or by airplanes, with a survival rate
of 80% or higher of the designed number of trees per hectare, or with a canopy density
of 0.20 or above after 3-5 years of
manual planting or 5-7 years of airplane planting.
Forest Coverage Rate refers to the ratio of area of
afforested land to total land area. It is a very important indicator that
reflects the status of abundance of forest resource and balance of the
ecosystem. Forest area includes the area of trees and bamboo grow with canopy
density above 0.2, the area of shrubby tree according to regulations of the
government, the area of forest land inside farm land and the area of trees
planted by the side of villages, farm houses and along roads and rivers. The
formula for calculating forest coverage rate is as follows:
![]()
Total Standing Stock Volume refers to the total stock volume of
trees growing in land, including trees in forest, trees in sparse forest,
scattered trees and trees planted by the side of villages, farm houses and
along roads and rivers.
Stock Volume of Forest refers to total stock volume of wood
growing in forest area, which shows the total size and level of forest
resources of a country or a region. It is also an important indicator
illustrating the richness of forest resource and the status of forest
ecological environment.
Total Area of Afforestation refers to the total area of land suitable for afforestation,
including barren hills, idle land, sand dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland
and “grain for green” land, on which acres of forests, trees and shrubs are
planted through manual planting.
Manual Planting refers to technical measures
of sowing, planting seedlings and divided transplanting on land suitable for afforestation, including barren hills, idle land, sand
dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland and “grain for green” land to increase
vegetation coverage rate of forests.
Airplane Planting refers to technical
measures of airplane planting with of appropriate artifical
help taken under the influence of natural power to restore certain amount of
seedlings on land suitable for afforestation,
including barren hills, idle land, sand dunes, non-timber forest land, woodland
and “grain for green” land, with an aim of increasing vegetation coverage rate
of forests.
Mountain-closuring &
Re-planting of
Timber Forests refer to forests which
are mainly for the production of timber, including bamboo groves planted to
harvest bamboos.
By-product Forests refer to forests that
mainly produce fruits, nuts, edible oil, beverages, indigents, raw materials
and medicine materials. By-product forests are planted to harvest the fruits,
leaves, bark or liquid of trees, and consume them as food or raw materials for
the manufacturing industry, such as tea-oil trees, tung
oil trees, walnut trees, camphor trees, tea bushes, mulberry trees, fruit
trees, etc.
Protection Forests refer to forests,
trees and bushes planted mainly for protection or preservation purpose,
including water resource conservation forests, water and soil conservation
forests, windbreak and dune-fixing forests, farmland and pasture protection
forests, riverside protection forests, roadside protection forests, etc.
Fuel Forests refer to forests planted
mainly for fuels.
Forests for Special Purpose refer to forests
planted mainly for national defence, environment protection or scientific
experiments, including national defence forests, experimental forests,
mother-tree forests, environment protection forests, scenery forests, trees in
historical or scenic spots, forests in natural reserves.
Project on Preservation of Natural Forests
is the Number One ecological project in
Projects on Converting Cultivated Land to Forests and Grassland (Grain for
Green Projects) aiming at preventing soil
erosion in key regions, these projects are ecological construction projects in
the development of forest industry that have the widest coverage
and most sophisticated procedures, with strong policy implications and most
active participation of the people.
Projects on Protection Forests in North China and Yangtze River Basin covering the widest areas in China with a rich variety of
contents, these projects aim at solving the problem of sand and dust in northeastern China, northern China and northwestern
China and the ecological issues in other areas. More specifically, they include
phase IV of Project on North China protection forests, phase II of Project on
protection forests at the middle and lower streams of Yangtze River and at the Huihe River and Taihu Lake
valley, phase II of Project on coastal protection forests, phase II of Project
on Pearl River protection forests, phase II Project on greenery of Taihang Mountain and phase II Projects on greenery of plains.
Projects on Harnessing Source of Sand and Dust in Beijing and
Tianjin these Beijing-ring projects aim at
harnessing the sand and dust weather around
Projects on Preserving Wild Animals and Plants and on Construction of
Natural Reserves aiming at gene preservation and
protection of bio-diversity, nature and wetlands, these projects are
forward-looking with strategic perspectives in line with international trends
and practices.
Projects on Fast-growing Timber Forests Bases in Key Regions are key projects for the forest industry to strengthen its
capacity in supplying more timber and forest by-products.
Wetlands refer to marshland and
peat bog, whether natural or man-made, permanent or temporary; water covered
areas, whether stagnant or flowing, with fresh or semi-fresh or salty water
that is less than 6 meters deep at low tide; as well as coral beach, weed
beach, mud beach, mangrove, river outlet, rivers, fresh-water marshland,
marshland forests, lakes, salty bog and salt lakes along the coastal areas.
Mangrove refers to evergreen woody
plants or plant communities in tropical or sub-tropical zones which live
between the sea and the land in areas which are inundated by tides.
Natural Reserves refer
to certain areas of land, waters or sea demarked and approved by relevant
governments at all levels to put under special protection and management in
order to protect the natural environment and natural resources and to promote the
sustainable development of the national economy.
According to the objects be protected, the natural reserves are classified into
classes of natural ecosystem, wild life and natural heritage. Scenic spots and
cultural preservation zones are not included.
Landslides refer to the geological
phenomenon of unstable rocks and earth on slopes sliding down along certain
soft surface as a result of gravitational force. Role of surface water and
underground water, and destruction of the stability of slopes by irrational
construction work are usually main factors triggering landslides. Severe
damages are often caused by landslides in open mining, in water conservancy
projects, and in the construction of railways and highways.
Collapse refers to the geological
phenomenon of large mass of rocks or earth suddenly collapsing from the
mountain or cliff as a result of gravitational force. Usually caused by
weathering of rocks, permeance of rain or
earthquakes, collapse often destructs buildings and blocks river course or
transport routes.
Mud-rock Flow refers to the sudden
rush of flood torrents containing large amount of mud and rocks in mountainous
areas. It is found mostly in semi-arid hills or plateaus. High and precipitous
topographic features, loose soil mass, heavy rains or melting water contribute
to the mud-rock flow.
Land Subside refers to the geological
phenomenon of surface rocks or earth subsiding into holes or pits as a result
of natural or human factors. Land subside can be classified as karst subside and non-karst
subside.
Sudden Accidents Effecting Environment
refer to sudden accidents, due to economic or social activities that are
contrary to environment protection laws or due to unforeseen factors or natural
disasters, that lead to environment pollution, destruction of protected wild
animals, plants or nature reserves, damage to human health, economic and
property losses, and other negative impacts on the society.
Investment in Environment Pollution Harnessing Projects refers to the proportion of investment in fixed assets in the total
investment in harnessing pollution and in the construction of urban environment
infrastructure facilities. The investment in harnessing pollution It includes
investment in harnessing sources of industrial pollution and investment in
environment protection facilities designed concurrently with construction projects.
Investment in environment pollution harnessing is the total of investment in
harnessing pollution and investment in urban environment infrastructure
facilities.
Funds Allocated to Afforestation refers to the total funds which have
been transfered into the specific accounts of the
agencies responsible for afforestation projects at
reporting period.
Completed Investment for Afforestation during the Year reflecting the actual size of investment completed during
January 1 and December 31 of the reference year, this indicator is important in
estimating investment efficiency and in making annual analysis of the
performance of the national economy.