Explanatory Notes on Main Statistical Indicators
![]()
Notary Personnel refers to people working
for notary offices including: directors, deputy directors, notaries, assistant
notaries and other people providing assistance.
Notary Documents refer to the judicial
notary documents drawn up at the request of the interested party and are in
accordance with facts and the law and following certain legal proceedings.
Extraordinarily Serious Traffic
Accident
refers to an accident which has caused three or more deaths; or over 11 serious
injuries; or one death and over 8 serious injuries; or two deaths and over 5 serious
injuries; or a loss over 60 thousand yuan.
Serious Traffic Accident refers to an accident
which has caused one or two deaths; or three to ten serious injuries; or a loss
over 30 thousand yuan to 60 thousand yuan.
Extraordinarily Serious Fire Case refers to a case which
has caused over 30 deaths; or over 100 serious injuries; or a direct property
loss over 100 million yuan.
Serious Fire Case refers to a case which
has caused over 10 to 30 deaths; or over 50 to 100 serious injuries; or a
direct property loss over 50 million to 100 million yuan.
Comparatively Serious Fire Case refers to a case which
has caused over three to ten
deaths; or over 10 to 50 serious injuries; or a direct property loss over 10
million to 50 million yuan.
Ordinary Fire Case refers to a case which
has caused less than three deaths; or less than 10 serious injuries; or a
direct property loss less than 10 million yuan.
Cases Registered and Handled Directly
by People’s Procuratorate Offices refer to those serious
criminal cases that, according to the functional jurisdiction, are registered
and handled by the People’s Procuratorate Offices,
including the ones on bribery and corruption, the ones on abuse and dereliction
of duty, offences against citizens’ personal and democratic rights by
government officials abusing their powers; and that are registered and handled
by the provincial Procuratorate offices in relation to other major crimes
committed by government officials by abusing their powers.
Key Cases refer to crimes committed by county
and director-level officials. This indicator reflects the situation of those
county and director-level officials involved in criminal cases registered and
handled by People’s Procuratorate offices.
Approval for Arrest refers to the decision
made by people’s procuratorate office, in accordance
with the law and relevant facts, to approve the arrest of the suspect(s) as
proposed by the public security departments, state security departments or
prisons authority. This indicator reflects approved arrests made by people’s procuratorate offices that are proposed by related
departments.
Decision on Arrest refers to decision made
by the people’s procuratorate office, in accordance
with laws, to arrest the suspect(s) in the cases that are accepted and to be
investigated by procurators office. This indicator mainly reflects the
implementation of the decision on arrest by people’s procuratorate
office.
Cases by Public Prosecution refer to those ones that
are instituted by People’s Procuratorate offices
after their examination of such cases transferred by public security organs,
national security organs, jail management organs and prosecutorial organs on
the bases of the facts found. This indicator reflects the situation of public
prosecutions instituted to the people’s courts by People’s Procuratorate
Offices.
Summary Procedure refers to those cases of
public prosecution where the suspects might be, according to law, sentenced to
fixed-term imprisonment of not more than three years, criminal detention,
public surveillance or punishment with fines exclusively, where the facts are
clear and the evidence is sufficient, and for which the People's Procuratorate suggests or agrees to the application of
summary procedure; those cases to be handled only upon complaints; and those
minor criminal cases prosecuted by the victims with evidence.
Protests Presented refers to those protests
presented by local People's Procuratorate at any
level who considers that there exists some definite error in a judgment or
order of first instance made by a People's Court at the same level to the
People's Court at the next higher level, including the protests raised in
accordance with the second instance and protests raised in accordance with
procedure for trial supervision.
Withdrawal of Protests refers to the actions
made by the People's Procuratorate at the next higher
level when it considers the protests inappropriate by withdrawing the protests
from the People's Court at the same level and notifying the People's Procuratorate at the next lower level.
Case Registration Supervision refers to the actions
made by the People's Procuratorate to supervise the
registration of criminal cases initiated by investigative authorities,
including supervision of the cases which have wrongly not been registered and
have wrongly been registered.
Supervision of Case Registration includes both the
supervision of those registrations initiated by investigatory authorities and
the supervision of those registrations according to notifications after hearing
declined reasons for registration.
Supervisory Activities refers to the supervision
of the People’s Procuratorate over the management of
prisons as well as other places of criminal reformation under supervision.
Juvenile Criminals refers to the offenders
within the age range of 14 to 25 convicted guilty by the court during the
reporting period while those between 14 and 18 are defined as minor offenders.
Administrative Cases refers to the cases filed
by citizens, corporations and other organizations against the specific
administrative conducts of administrative authorities and handled by the court.
Separate Compensation refers to cases that are
separately filed for administrative compensation by the party who has no
dispute on the legality of administrative conducts but brings proceedings
separately to claim for damages caused by administrative tort.
Number of Urban Residents Entitled to
Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those whose average family income is
below a minimum local standard by the end of the reporting period, including
both the employed and unemployed, laid off and retired, and those jobless
people without stable residence or valid IDs.
Number of Rural Residents Entitled to
Minimum Living Allowances refers to the number of those receiving the minimum living
allowances from the local government or community in the rural areas where this
allowances system is in place as of the end of the reporting period.
Households Enjoying Five Guarantees refers to those senior
citizens, handicapped or under-aged who, without labour
ability, can not make a living by themselves and whose statutory providers are
unable to support them or who have no statutory providers at all.
Number of Rural Recipients of
Traditional Relief refers to the poor people entitled to traditional relief in
rural areas where the minimum living allowances system is not in place.
Social Welfare Enterprises refers to those
welfare-oriented enterprises employing a significant number of handicapped
people with certain labour ability (handicapped
employees shall exceed 10% of the production staff), including welfare
factories, artificial limb plants as well as other welfare enterprises.
Number of Service Facilities in Urban
Communities refers to the number non-profit welfare facilities set up by urban
communities (community offices and residents’ committees) to serve the
community residents, including, among others, community-based centers that
serve senior citizens, the handicapped or children, recreational centers,
service centers, nursing homes, apartments for the elderly (nursery for the
aged), work and treatment stations for the handicapped, day-care centers for
handicapped children, domestic help agencies and dating services, as well as
social insurance management agencies for the employees. Different types of
community service providers that share the same premise are regarded as one
community service facility. The requirements for a social service facility of
communities include: (1) independent accounting; (2) fixed employees; (3)
provision of services; and (4) premises.
Crude Divorce Rate refers to ratio of
divorced couples to the annual average population for the reference year, the
formula is:
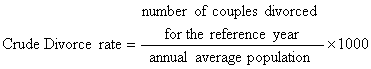
Proportion of Deaf Children Enrolled
in Ordinary Pre-school and Primary Education refers to the proportion of deaf
children who are enrolled in ordinary kindergartens or primary schools during
the year in the total number of deaf children under rehabilitation programme (not including new comers into the rehabilitation
programme during the year).
Number of Mental Patients under the
Integrated Prevention and Rehabilitation Programme refers to mental disease
patients receiving integrated prevention and rehabilitation treatment of
various forms under open environment in areas with mental disease
rehabilitation programmes. This indicator reflects
the situation of mental patients receiving rehabilitation treatment.
Supervision Rate refers to the percentage
of patients among the total number of registered mental disease patients, who
participate in social integrated and open treatment and rehabilitation programmes through various forms such as supervision
groups, family treatment, employment or guidance from psychiatric institutions.
This indicator reflects the implementation of various measures aimed at
rehabilitating those mental patients.
Social Participation Rate refers to proportion of mental
disease patients who are able to manage their daily life and participate in
economic activities to the total number of mental disease patients under
supervision. This indicator reflects the condition of recovery of those mental
patients and their participation in social activities.
Violation Rate refers to the number of
the patients with mental diseases who have violated the Public Security
Regulations as a percentage of the total registered patients with mental
diseases within the year.
Total Number of Handicapped
School-age Children without School Attendance refers to the number of handicapped
children of the school age as prescribed by the provincial government in
accordance with the Law on Compulsory Education who fail to attend any schools
for various reasons as of December 31 of the current year.
Centralized Employment refers to the number of
the urban handicapped residents employed, in a centralized manner, by welfare
enterprises, work and treatment agencies, blind massagists’
centers and other organizations as of December 31of the current year.
Proportionate Employment refers to the number of
the urban handicapped residents employed by governmental bodies, organizations,
corporate and public institutions, and various economic organizations in a
decentralized manner as of December 31 of the current year.
Number of Labour
Disputes Cases Accepted refers to the number of cases of labour
disputes submitted that, after being reviewed by the labour
dispute arbitration committees in line with the relevant national regulations, are accepted and registered for treatment.
Basic Pension Insurance
1.Number of staff and workers covered refer to staff and workers
participating in the basic pension insurance programme
according to national laws, regulations and related policies at the end of the
reference period, who have already had payment records in social security
management agencies, including those who have interrupt payment without
terminating the insurance programme. Those who have
registered in the programme but with no payment
records are not included.
2. Number of retirees participating
in the basic pension insurance programme refer
to the number of retirees participating in basic pension insurance programmes by the end of the reference period.
3. Revenue of the basic pension
insurance programme refers to payments made by employers
and individuals participating in the pension insurance programme
in accordance with the basis and proportion stipulated in State regulations,
and income from other sources that become source of pension insurance fund,
including the premium paid by employers and staff and workers, interest income,
subsidies from higher level agencies, income as transfer from subordinate agencies,
transferred income, government financial subsidies and other income.
4. Expenditure of basic pension
insurance programme refers to payment made on pensions
and funeral subsidies to those retired and resigned people covered in pension
insurance programmes according to related national
policies on scopeand standard of expenditure. Also
included are expenditure which arises due to shift of
the insurance relationship or adjustment of funds among agencies. More
specifically, included are pensions
for resigned people, pensions for retired people, pension for people quitting
jobs, various subsidies, medical fees, funeral subsidies, compensation
payments, management fees for social security agencies, expenses on subsidies
to lower subordinates, expenses as transfer to agencies at higher level,
transferred expenditure and other expenditure.
5. Balance of basic pension insurance
programme refers to the balance of basic
pension insurance funds at the end of the reference period after deducting
expenses from revenue.
Basic Medical Care Insurance
1. Number of people participating in
the insurance programme refers to people participating in
the basic medical care insurance programme according
to related regulations as at the end of reference period, including number of
staff and workers and retirees participating in this insurance programme.
2. Revenue of the insurance programme refers to payments made by employers and individuals
participating in the medical care insurance programme
in accordance with the basis and proportion stipulated in State regulations,
and income from other sources that become source of medical insurance fund,
including income of social comprehensive funds paid by employers, income from
individual accounts, government financial subsidies, interest income and other
income.
3. Expenditure of the insurance programme refers to payment made from social comprehensive funds to
those retired and resigned people covered in basic medical care insurance
within the scope and standards of expenditure according to related national
policies, and medical care payment made from individual accounts to staff and
workers and retirees, and other expenses, including medical expenses of
hospital inpatients, medical expenses for outpatients and emergency patients,
payment from individual accounts and other expenditure.
4. Balance of the basic medical care
insurance programme refer to the balance of medical care
insurance of social comprehensive funds and individual accounts at the end of
the reference period, including bank savings, special fiscal accounts,
investment in bonds and others.
Unemployment Insurance
1. Number of people covered refers to staff and
workers in urban enterprises or institutions who have participated in the
unemployment insurance programme according to
relevant policies and regulations, and other people who have participated
according to local government regulations, as at the end of reference period.
2. Revenue of the unemployment
insurance programme refers to payments made by employers
and individuals participating in unemployment insurance programme
in accordance with relevant regulations and other income contributed to this programme, including unemployment insurance premium made by
employers and individuals, interest income, subsidies from higher level
agencies, income as transfer from subordinate agencies, transferred income,
government financial subsidies and other income.
3. Expenditure of the unemployment
insurance programme refers to total expenses during the
reference period to guarantee the basic livelihood of unemployed people and
laid-off staff and workers and to encourage their re-employment. Included are
unemployment relief, medical fees, funeral subsidies, compensation payments,
training expenses, management fees for unemployment insurance agencies,
subsidies to lower level agencies, expenses as
transfer to higher level agencies, transferred expenditure and other
expenditure.
4. Balance of the unemployment
insurance programme refers to the balance of revenue of
the programme after deducting expenses at the end of
the reference period.
Work Injury Insurance
1. Number of people covered refers to staff and
workers who have participated in the work injury insurance programme
according to relevant national regulations.
2. Number of beneficiaries refers to staff and
workers and their direct dependents who can, in
accordance with relevant regulations, benefit from work injury insurance, as a
result of work injury leading to disability or death of the staff/worker, or
occupational disease leading to disability. Included in this category are
number of injured and disabled people, number of people with occupational
diseases, number of deaths at work places, and number of direct dependents.
3. Revenue of the work injury
insurance programme refers to payments made by employers
participating in the work injury insurance programme
in accordance with the basis and proportion stipulated in State regulations,
and income from other sources that become source of work injury insurance fund,
including income of social comprehensive funds paid by employers, government
financial subsidies, interest income and other income.
4. Expenditure of the work injury
insurance programme refers to payments made from work
injury insurance funds to those who participated in the work injury insurance programme and their direct dependents within the scope and
standards of expenditure according to related national policies, and other
expenditure, including medical fees for work injury, injury and disability
subsidies, death subsidies, nursing fees, funeral subsidies, injury prevention
fees, occupational rehabilitation fees and other expenditure.
5. Balance of the work injury
insurance programme refers to the balance of the work
injury funds at the end of the reference period, including bank savings,
special fiscal account, investment in bonds and others.
Maternity Insurance
1. Number of people covered refers to staff and
workers who have participated in the maternity insurance programme
according to relevant regulation at the end of the reporting period.
2. Revenue of maternity insurance refers to payments made
by employers participating in the maternity insurance programme
in accordance with the basis and proportion stipulated in State regulations,
and income from other sources that become source of maternity insurance fund,
including income of funds paid by employers, interest income and other income.
3. Expenditure of the maternity
insurance programme refers to payments made from
maternity insurance funds to staff and workers who participate in the maternity
insurance programme within the scope and standards of
expenditure in accordance with related national policies, expenses paid for
pregnancy, child delivery or surgeries related to family planning, and other
expenditure, including allowance for child bearing, medical fees and other
expenditure.
4. Balance of the maternity programme refers to the balance of the maternity insurance funds at
the end of reference period, including bank savings, special fiscal account,
investment in funds and others.